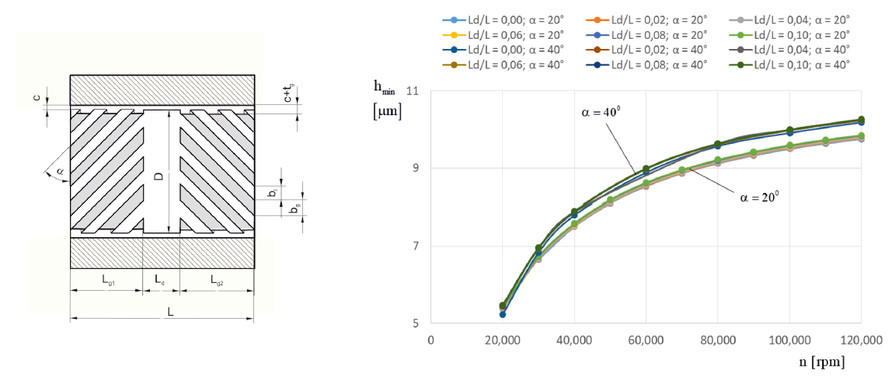
Aerodynamic or gas-lubricated bearings are applicable for the support of high-speed rotating shafts due to the low friction in the gas-lubricated film gap and the absence of contaminants in the lubricant. In general, foil bearings, segmented spring bearings, or spiral grooved bearings can be used. Spiral grooved bearings exhibited high load capacity; thus, spiral grooved bearings were the subject of the investigations. Herringbone-grooved journal bearings (HGJBs) generate a pressure field in the lubricating gap between the rotating shaft and the sleeve due to the pumping effect of the inclined grooves. For reliable operation of the rotor bearing system, stable operation in the whole speed range (up to 120 krpm), as well as low lift-off speed, is an important issue. Both optimization targets—lift-off speed and stability threshold speed—lead to different “optimum” bearing designs because good lift-off behavior is realized with a low groove inclination angle (at about 20°), whereas stability can only be achieved with higher groove inclination angles (α = 40°). The stable operation must always be ensured (representing a necessary condition); therefore, the focus of the optimization procedure was on optimizing the parameters for optimum stability.
H. Schlums, C. Hühne, M. Sinapius
Design of a Herringbone-Grooved Bearing for Application in an Electrically Driven Air Compressor
Machines 2022, 10(8), 662; (2022) [Link]