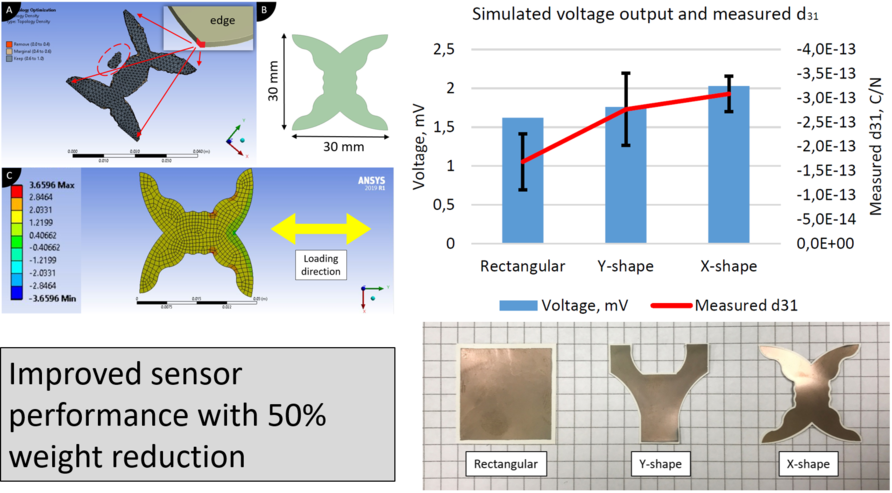
By adopting topology optimization based on numerical solvers, the geometries of the piezoelectric sensors can be optimized to produce higher electrical output in a certain loading directions. 2D topology optimization and simulation studies are carried out with ANSYS using Piezo and MEMS extensions for coupled systems. Topology optimization is based on Solid isotropic material with the penalization method, where the design variables are the pseudo densities that control material distribution at each finite element. The optimization problem is solved using Sequential Convex Programming. The approximation of the objective function happens through a uniform convex function. The objective is to reduce the fundamental frequency of the piezoelectric sensor for given constraints and boundary conditions (maximum sensor size of 30 × 30 mm and reduction of sensor mass by 50%). Two optimized shapes are chosen for further analysis. All sensors are made of 10 vol% PZT piezoelectric ceramic in High-Temperature V2 photopolymer resin. Sensors are manufactured using a simulated Direct Light Processing (DLP) type 3D printing process by tape-casting them on glass and exposing them to UV light. The performance of sensors is measured on a 4-point bending setup. Experiments show the enhanced performance of the optimized sensors even when their mass is reduced by 50%.
R. Mitkus, A. Alashkar, M. Sinapius
An Attempt to Topology Optimize 3D Printed Piezoelectric Composite Sensors for Highest D31 Output
SMASIS2021-68029, V001T06A006; (2021) [Link]