The 6G Research and Innovation Cluster (6G-RIC) aims to lay the scientific and technical foundations for the next generation of mobile networks (6G) across all technology levels, including radio access, core and fibre optic transport networks. Through cutting-edge research and international networking, 6G-RIC will help to establish Germany as a leading global business location for sustainable 6G technologies.
As an Alexander von Humboldt Fellow, Aaron Becker is a visiting professor with Professor Sándor Fekete in the Group Algorithms at the Institute of Operating Systems and Computer Networks. Becker's research focuses on finding out how tiny swarm robots could be used for operations in medicine in the future.
The aim of the research training group is to create the scientific basis for a circular economy and the production of lithium-ion batteries in Lower Saxony. In order to achieve carbon neutrality and thus limit the effects of climate change, private transport must be converted from combustion engines to battery-electric drives. It is therefore of the utmost importance to accelerate the research and development of batteries and at the same time increase battery production capacities.
The project "Deep Learning for Imaging Nano and Quantum Science" brings together expertise from applied physics and machine learning in the core research area of metrology to evaluate imaging methods in physics with artificial intelligence.
The core objective of the work planned in the EXDIMUM project is to examine extreme water management in the spectrum of complex challenges (little vs. much water, supra-regional vs. local area, long vs. short time spans, mountain slopes vs. lowlands, different land use with forest, mining, agriculture and urban areas) through the holistic interaction of data collection and modelling on multiple scales and derived measures. This includes in particular the use of satellite images with high temporal and spatial resolution, the inclusion of digital terrain models and the targeted, reliable collection of terrestrial sensor data.
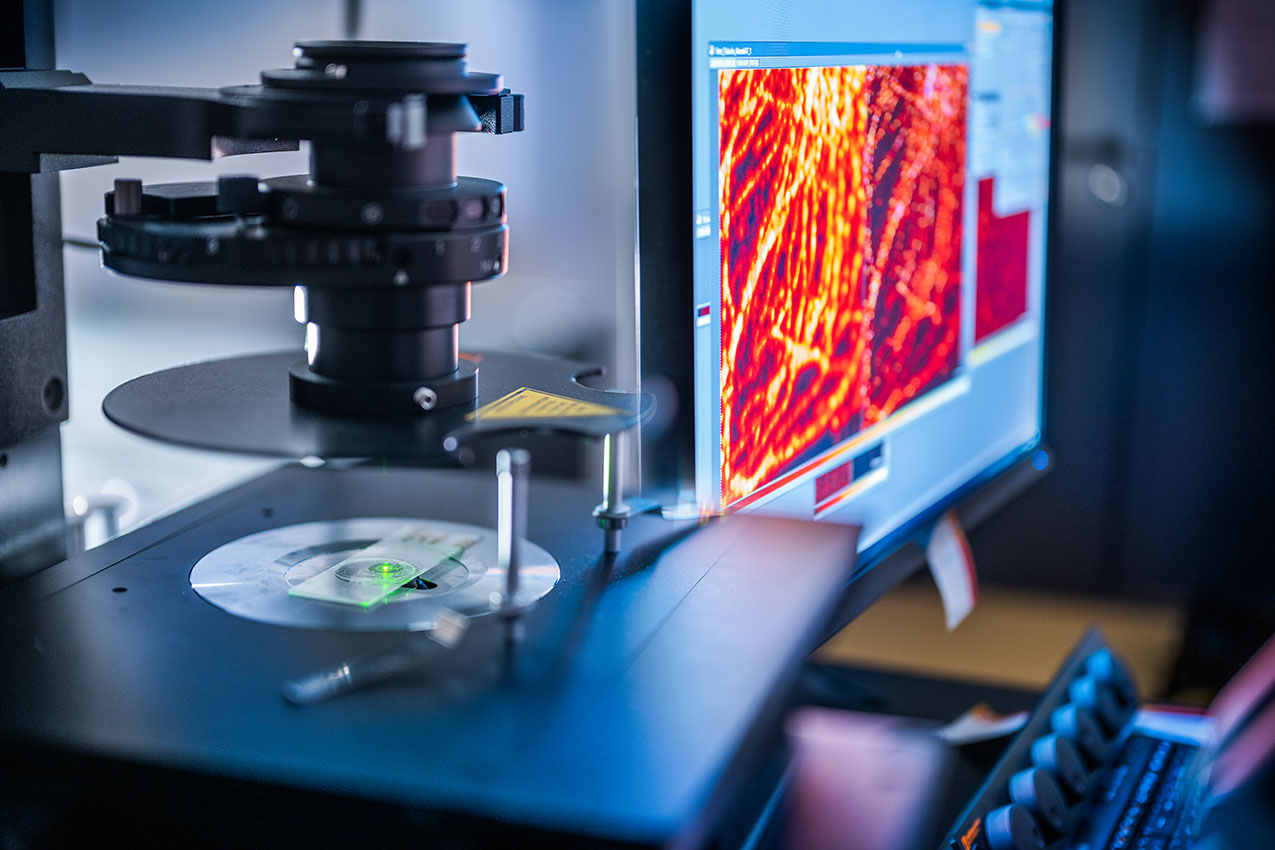
The latest neurological studies show that ageing processes in the brain in particular, which are accompanied by an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, ALS, Parkinson's disease), have their common cause in a dysfunctional homeostasis of brain cells. The scientists involved in the Homeo-Hirn project are investigating how the sub-compartments of the nerve cells – cell bodies, dendrites, axons and synapses – interact with each other and with the glial cells and what effects a disturbed metabolic homeostasis, for example after an infection, has on the brain. In order to answer these complex questions, precise measuring instruments and optical systems are required, which are to be developed by an interdisciplinary research team that enables the analysis of partial compartments of neurons and their metabolome.
In the course of the energy transformation, DC grids are becoming increasingly important for the integration of renewable energies and the energy supply of modern industrial applications. The Smart Modular Switchgear II research project aims to develop and integrate an intelligent switching and protection concept that is adapted to the new challenges of DC grids. In the event of a fault, it should independently perform fault detection, characterisation, localisation and coordination of the switching action (selective switching).
Technische Universität Braunschweig and Leibniz University Hannover are jointly positioning themselves for a strong European future in microeleltronics with the “Wissenschaftsraum Mikroelektronik“ (Microelectronics Science Area). Funded by the Volkswagen Foundation and the Lower Saxony Ministry of Science and Culture (MWK), the two universities are pooling their research and teaching activities, including a new degree programme.